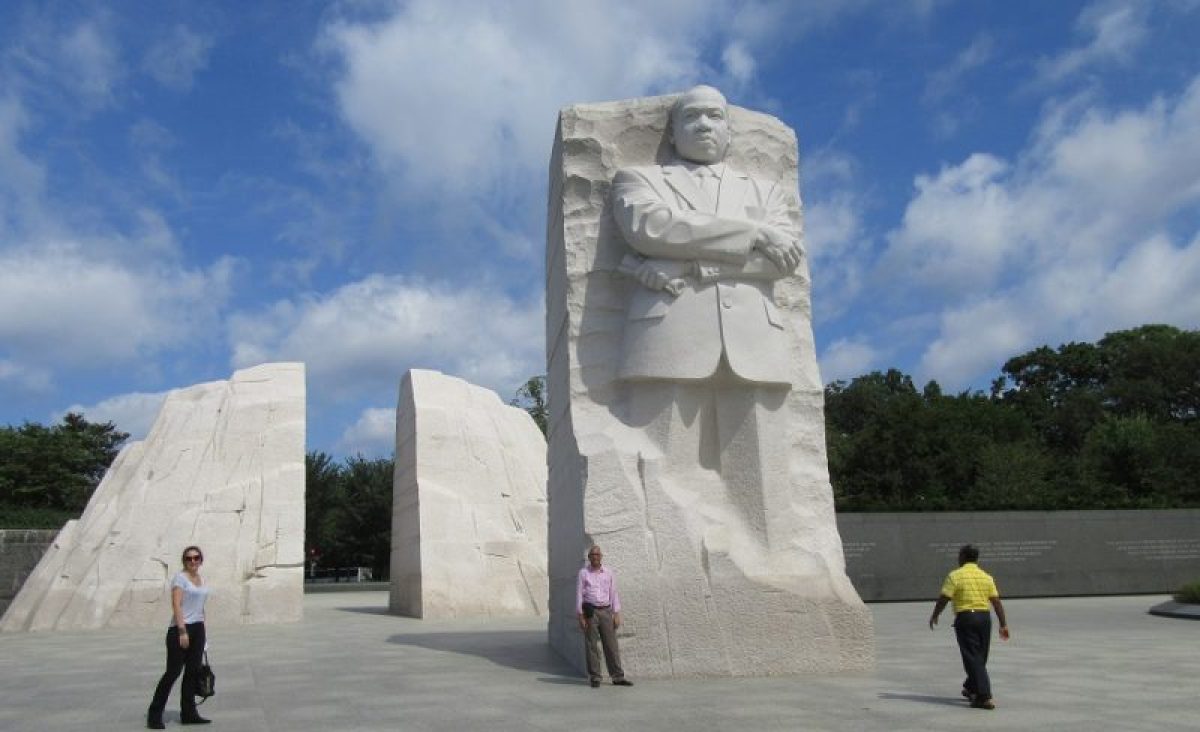
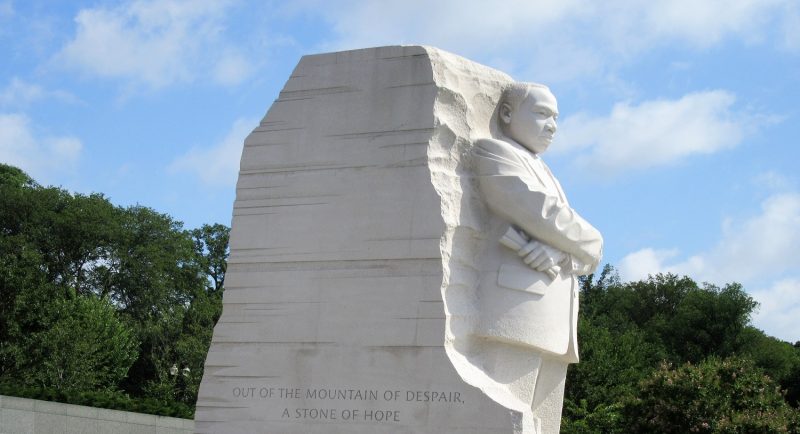
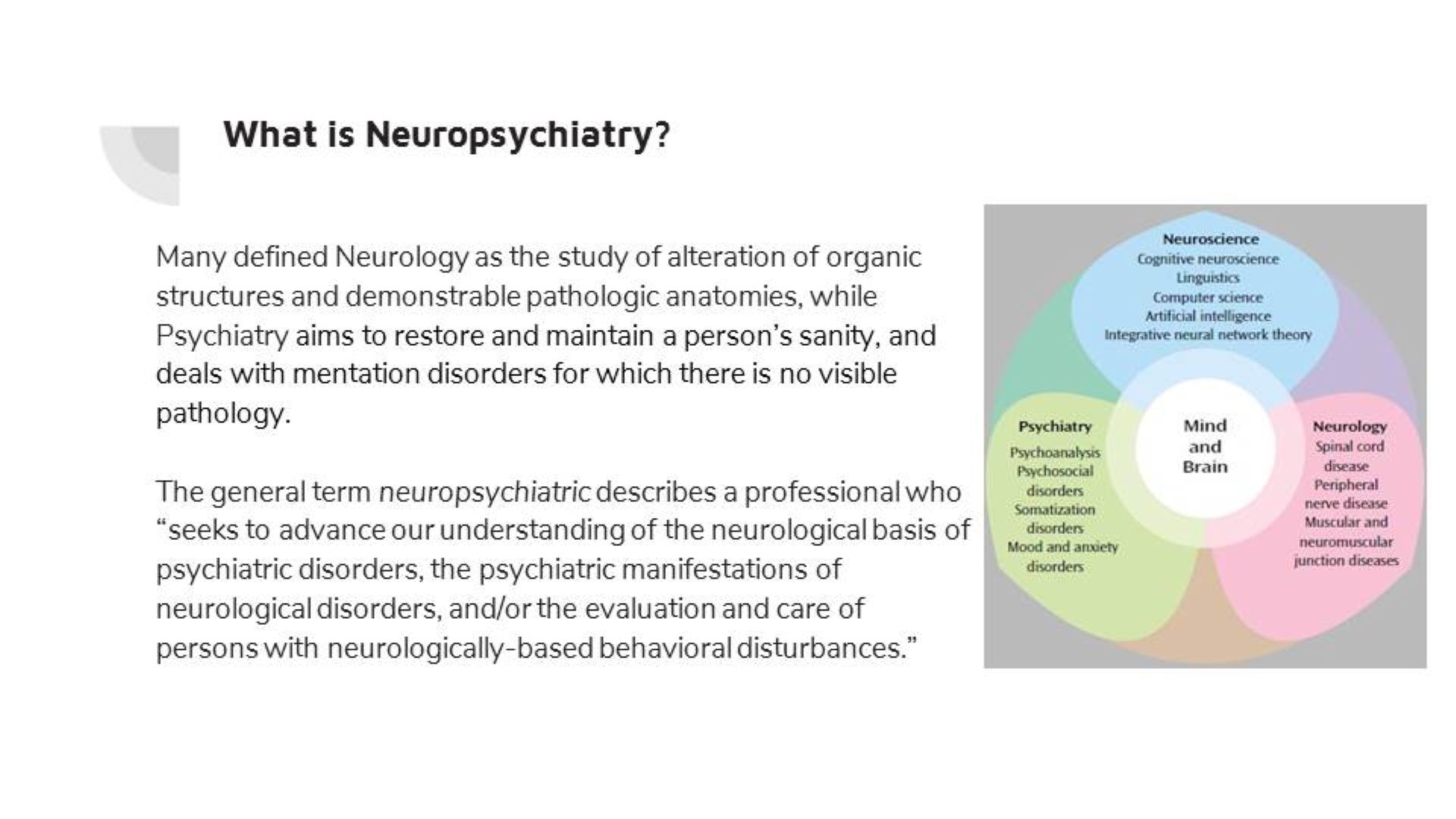
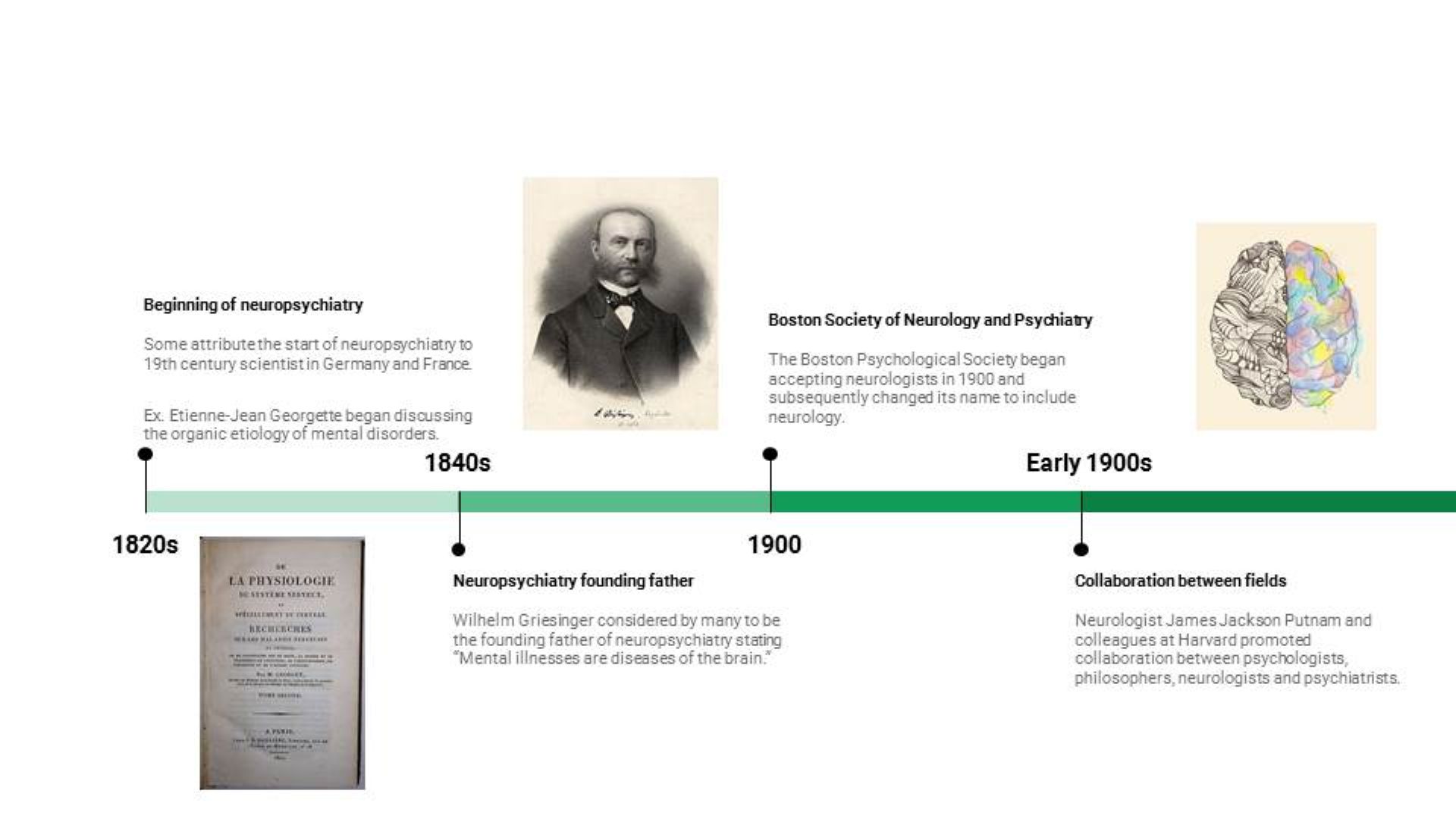
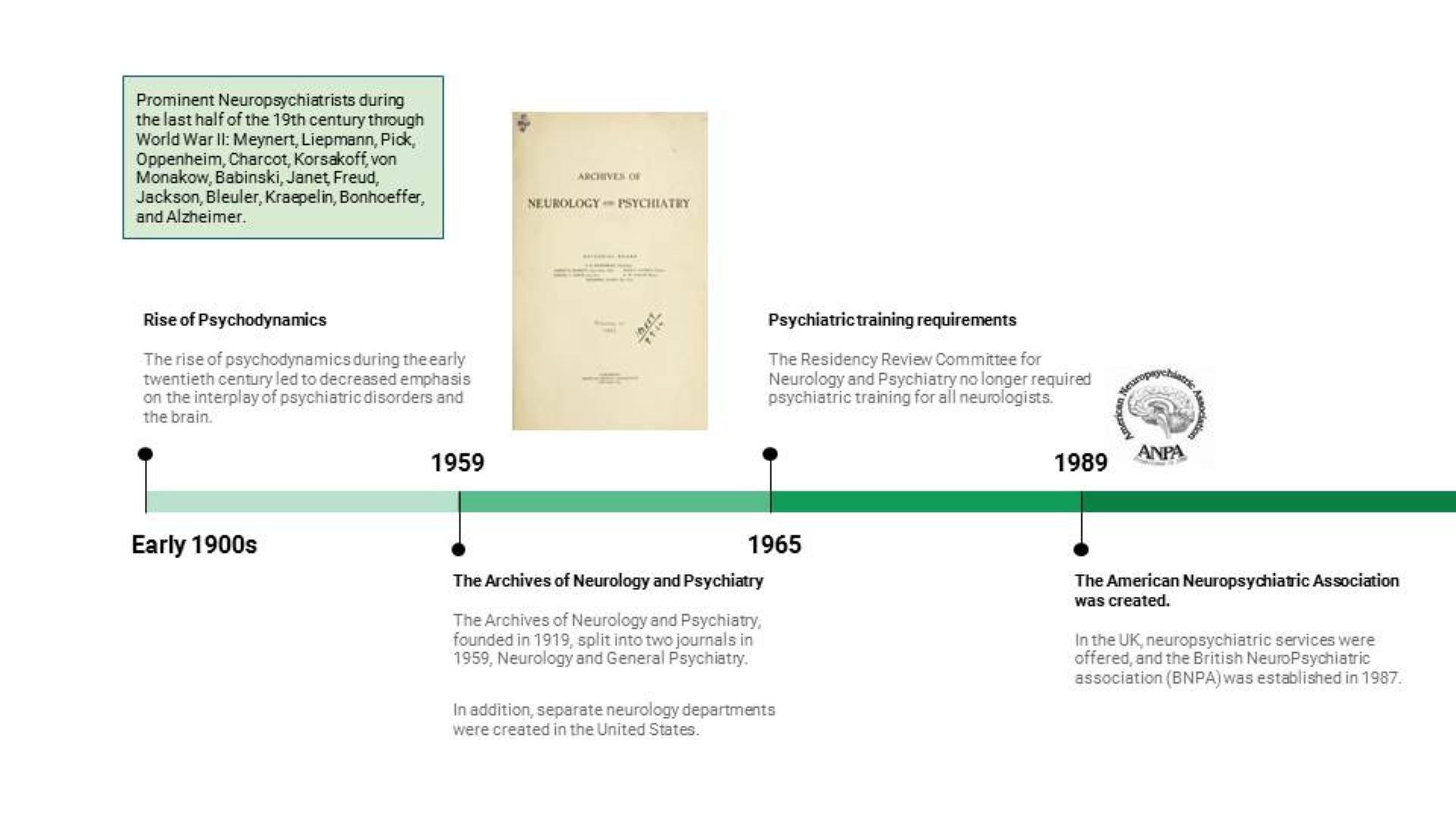
I ran across this quote from Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. in my notes:
“Human progress is neither automatic nor inevitable… Every step toward the goal of justice requires sacrifice, suffering, and struggle; the tireless exertions and passionate concern of dedicated individuals.”
― Martin Luther King Jr.
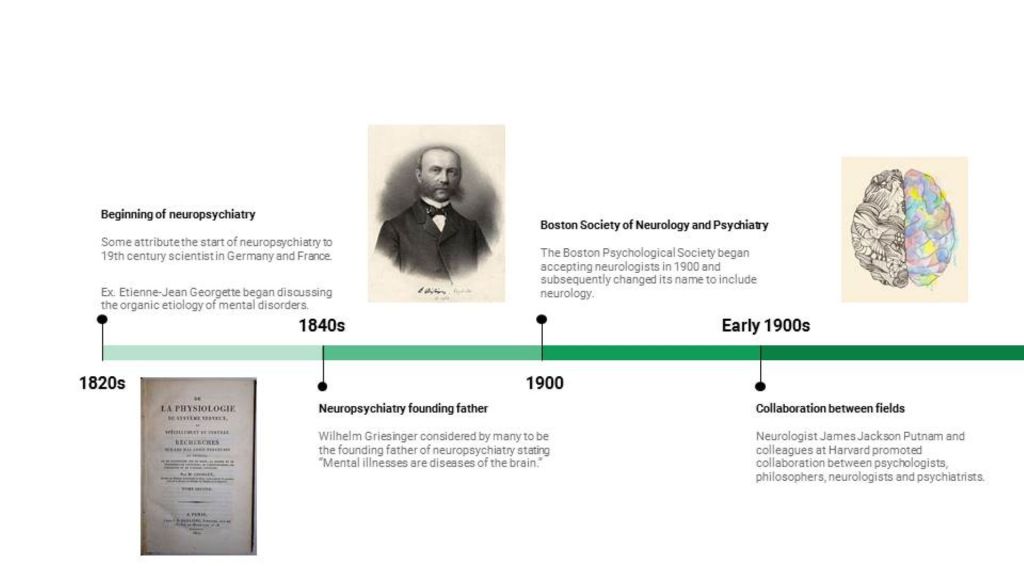
This week we’ll be getting the two biographies of Martin Luther King, Jr. One of them is a biography published a couple of years ago by Jonathan Eig, titled “King: A Life.” The other is an autobiography, “The Autobiography of Martin Luther King, Jr.”
This morning, I was focused on puzzling over Eig’s book, in which there is a focus of how depression affected Dr. King. Gradually, I found out more about his struggles with mental health than I ever knew, and people were aware of them many years before Eig.
Dr. King never shared his emotional problems with anyone while he was alive in order to avoid the stigma in those times. Initially I asked “Why?” type questions. Why does anyone dig into a person’s private health information? That’s called PHI for short and it’s not supposed to be readily available to just anybody. Health professionals know that.
And then I remembered something I learned gradually over the course of my career as a psychiatrist. It’s hard to frame useful answers to “Why?” questions. It’s often more helpful to ask “What?” questions, mainly because they lead to actionable replies about things we might need to change.
What did I do as a teacher before I retired from consultation-liaison psychiatry in order to train those who would improve on what I did?
I shared with my students what I thought would be most helpful to them in their careers going forward:
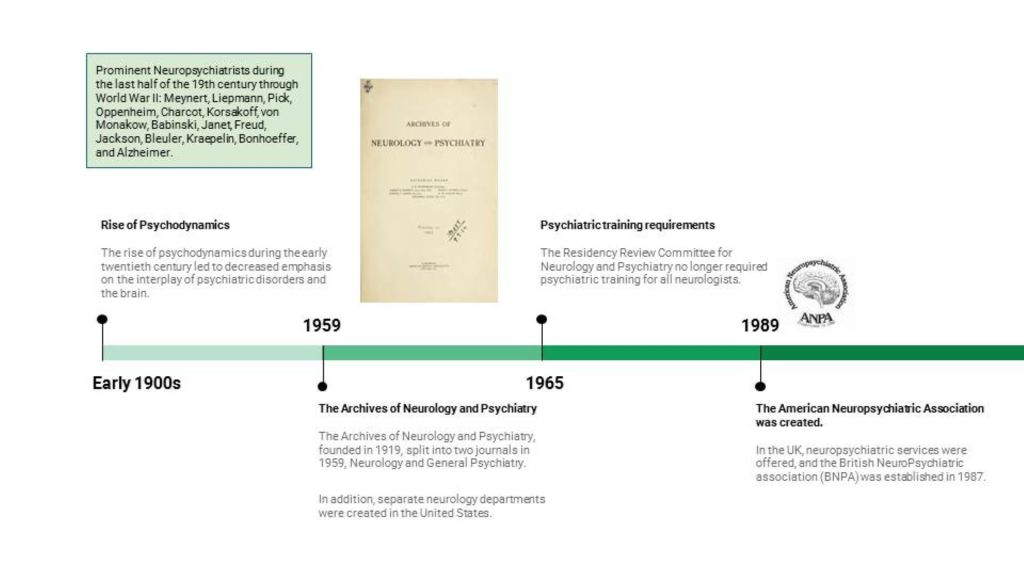
The shortage of psychiatrists in general, and of C-L psychiatrists specifically, still leads me to believe that George Henry was right when he said:
“Relegating this work entirely to specialists is futile for it is doubtful whether there will ever be a sufficient number of psychiatrists to respond to all the requests for consultations. There is, therefore, no alternative to educating other physicians in the elements of psychiatric methods.”– George W. Henry, MD, 1929 (Henry, G.W., SOME MODERN ASPECTS OF PSYCHIATRY IN GENERAL HOSPITAL PRACTICE. Am J Psychiatry, 1929. 86(3): p.481-499.)
There was so much in Henry’s paper published in 1929 that still sounds current today. I can paraphrase the high points:
- Practice humility and patience
- Avoid psychiatric jargon
- Stick close to facts; don’t get bogged down in theories
- Prevent harm to patients from unnecessary medical and surgical treatment, e.g. somatization
- “The psychiatrist deals with a larger field of medical practice and he must consider all of the facts.”
- The psychiatrist should “…make regular visits to the wards…continue the instruction and organize the psychiatric work of internes…attend staff conferences so that there might be a mutual exchange of medical experience”
- Focus on “…the less obvious disorders which so frequently complicate general medical and surgical practice…” rather than chronic, severe mental illness
The advantages of an integrated C-L Psychiatrist service (here I mean integrating medicine and psychiatry; mind and body) are that it increases detection of all mental disorders although that requires increasing the manpower on the service because of the consequent higher volume demand in addition to other requests, including but not limited to unnecessary consultation requests.
Further, what still astonishes me is the study which found that among consultee top priorities was an understanding of the core question (Lavakumar, M. et al Parameters of Consultee Satisfaction With Inpatient Academic Psychiatric Consultation Services: A Multicenter Study. Psychosomatics (2015). The irony is that the consultees frequently do not frame specific questions (Zigun, J.R. The psychiatric consultation checklist: A structured form to improve the clarity of psychiatric consultation requests. General Hospital Psychiatry 12(1), 36-44; (1990).
Moreover, it is sometimes necessary to give consultees bad news. A consultant should be able to tell a colleague what he or she may not what to hear. This principle is applicable across many disciplines and contexts. And it is best delivered with civility.
A former president of the ACLP said:
“A consultation service is a rescue squad. At worst, consultation work is nothing more than a brief foray into the territory of another service…the actual intervention is left to the consultee. Like a volunteer firefighter, a consultant puts out the blaze and then returns home… (However), a liaison service requires manpower, money, and motivation. Sufficient personnel are necessary to allow the psychiatric consultant time to perform services other than simply interviewing troublesome patients in the area assigned to him.”—Dr. Thomas Hackett.
I don’t think it’s too much to expect things to improve. Speaking of improvement, Stephen Covey called it “sharpening the saw,” one of the 7 habits of highly effective people. For this, The University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics C-L Psychiatry has the Clinical Problems in Consultation Psychiatry or CPCP. This was started by Dr. Bill Yates in the 1990s, and it was originally called Problem-based Learning. “PBL…emphasis on the development of problem-solving skills, small group dynamics, and self-directed methods of education…most common types of problem categories identified for the conference were pharmacology of psychiatric and medical drugs (28%), mental status effects of medical illnesses (28%), consultation psychiatry process issues (20%), and diagnostic issues (13%) …PBL conference was ranked the highest of all the psychiatry resident educational formats.”
- Yates, W. R. and T. T. Gerdes (1996). “Problem-based learning in consultation psychiatry.” Gen Hosp Psychiatry 18(3): 139-144.Yates, W. R. and T. T. Gerdes (1996). “Problem-based learning in consultation psychiatry.” Gen Hosp Psychiatry 18(3): 139-144.
- Covey, S. R. (1990). The seven habits of highly effective people: restoring the character ethic. New York, Simon and Schuster.
What did I do when burnout made me a less effective teacher? In 2012 I started getting feedback from colleagues and trainees indicating they noticed I was edgy, even angry, and it was time for a change.
After reflecting on the feedback from my colleagues and students, I enrolled in our university’s 8 week group Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) program. Our teacher debunked myths about mindfulness, one of which is that it involves tuning out stress by relaxing. In reality, mindfulness actually entails tuning in to what hurts as well as what soothes.
Maybe we should ask what helped Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. persevere in spite of the inner turmoil and external pressure.